Moving AV Processing Beyond the Matrix Switch
In our last installment, I explained some great features of the matrix switch that SDVoE has learned from. With these lessons at the front of mind, it should be clear how SDVoE delivers matrix switching without the matrix switch. But SDVoE systems deliver AV processing capabilities far beyond that of a matrix switch. Many SDVoE devices include a powerful AV processing unit which enables advanced functionality that is expensive or impossible to add to a traditional circuit switch-based architecture. Let’s take a look at these features in detail.
Video scaling
Scaling is the ability to convert any video resolution to any other. This capability ensures that the SDVoE platform can deliver any image to any destination, regardless of source and display. Scaling is relatively common on high-end matrix switches. However, in that architecture scaling always brings a one- or two- frame latency penalty. SDVoE scaling can work in less than three milliseconds. The ability to convert between formats with less than a frame of latency is why SDVoE is the leading choice for performance-sensitive applications such as medical and gaming.
Instant switching
Combining scaling capability with an IGMP multicast (free SDVoE Academy registration required) feature called “fast leave,” SDVoE receivers are capable of switching instantly between any two sources in the system. This means no more frustrating blanking between sources, and no more users worried their image might not come back. Implementing this capability in a matrix switch is possible but hugely expensive. Typically only broadcast-class SDI matrix switches offer this capability.
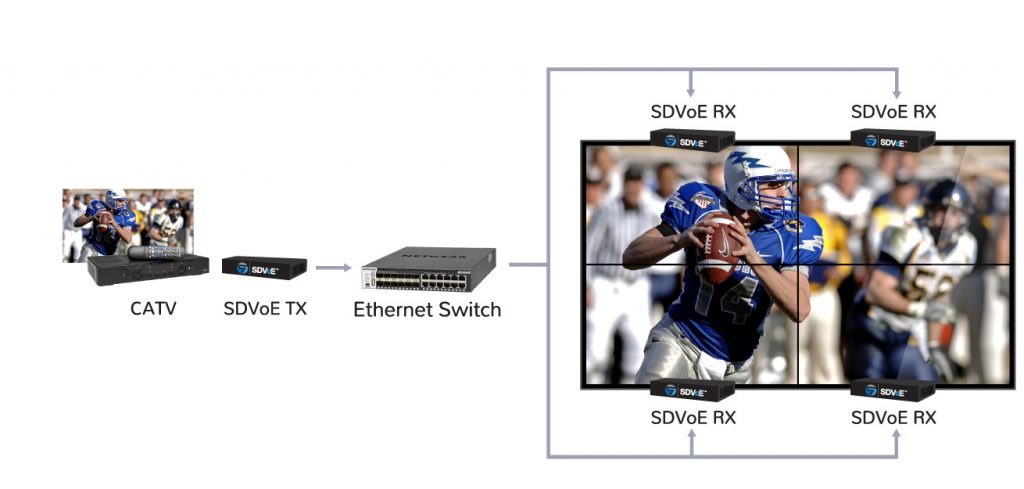
Image cropping: video walls
An SDVoE receiver can crop an image and focus only on a ‘region of interest.’ The receiver scales that region up to match the display’s resolution. This way, a single display presents only a section of a larger image. When combined with other SDVoE receivers and displays nearby, the effect is that of a single image stretched across a large canvas of multiple displays – a video wall. This is another feature that is available in more expensive matrix switch systems, but SDVoE is unique in that it can maintain timing synchronization between the multiple displays. The result of asynchronous video wall processing common to matrix switches is image tearing and geometry distortions. SDVoE eliminates these distortions by guaranteeing synchronization between displays.
Example of using multiple SDVoE receivers to create a synchronous video wall across multiple displays.
Multiview/compositing
The most sophisticated and unique image processing capability of SDVoE is the ability to take multiple images, scale and size them, and stitch them together on a single display. This is “picture in picture” on steroids – with the ability to create arbitrary layouts of up to dozens of images. Multiview is great for monitoring or collaboration applications. Before SDVoE, this capability was only available with an dedicated multi-window processor. Worse, you’d need one expensive processor for every display where multiview is needed.
Independent routing of audio and video
An SDVoE network carries every audio stream and video stream independently. Therefore audio and video can be routed separately from one another. SDVoE has an intricate clock synchronization system at its core, so lip sync is never a problem. Furthermore, manufacturers are already starting to integrate Dante networked audio transport into SDVoE endpoints, merging the best technology for video transport with the best technology for audio transport. Audinate is an SDVoE contributing member.
Audio downmixing
Ever have a 7.1 channel audio program that needs to reach a stereo-only destination? SDVoE has built-in audio downmix capability, so that multichannel zones can enjoy the full experience, and stereo zones can still join in. SDVoE can achieve this without expensive DSP hardware and licenses that drive up the cost of this capability. And the downmixed stream can of course be routed alongside the multichannel stream, each to a unique set of destinations.
USB transport
Through partnership with Icron Technologies (an SDVoE contributing member and the leading provider of USB extension and switching gear), many SDVoE products have USB switching seamlessly integrated, so your USB devices can be brought into the same switching environment as your audio and video. KVM is just the beginning, as these products can transport mass storage devices, web cams and microphones, and more.
What this all means
All of this capability is interesting, but why is it important? Because it creates flexibility. An SDVoE system can be configured and reconfigured, entirely via software, to suit a system owner’s ever evolving business needs. SDVoE can offer significant cost savings up front (compare the cost of an SDVoE receiver to a purpose-built video window processor!). But more significant are the cost savings over time, of a system that doesn’t need to be replaced every time a user’s needs change. SDVoE can meet your end customer’s needs today, and that same system can meet their needs tomorrow.